This document is a guide for migrating an existing wordpress website with live data to a docker container. The container will contain its own mysql, wordpress, and phpmyadmin images.
This guide is a continuation of the Dockerized Wordpress, MySQL, and phpmyadmin with environment variables article.
Pre-requisites
- Docker & Docker Compose
- Running wordpress docker instance (see: Dockerized Wordpress, MySQL, and phpmyadmin with environment variables article)
Obtain a copy of the wordpress site to migrate
-
Obtain a copy of the source code of the wordpress website to migrate using any methods you prefer (SSH, SFTP, webmin, etc.)
-
Obtain a copy of the website database with the .sql file extension using any methods you prefer.
Run the dockerized wordpress container
- Run a newly built dockerized wordpress-mysql-phpmyadmin container.
1 2
$ cd /mysite/ $ docker-compose up
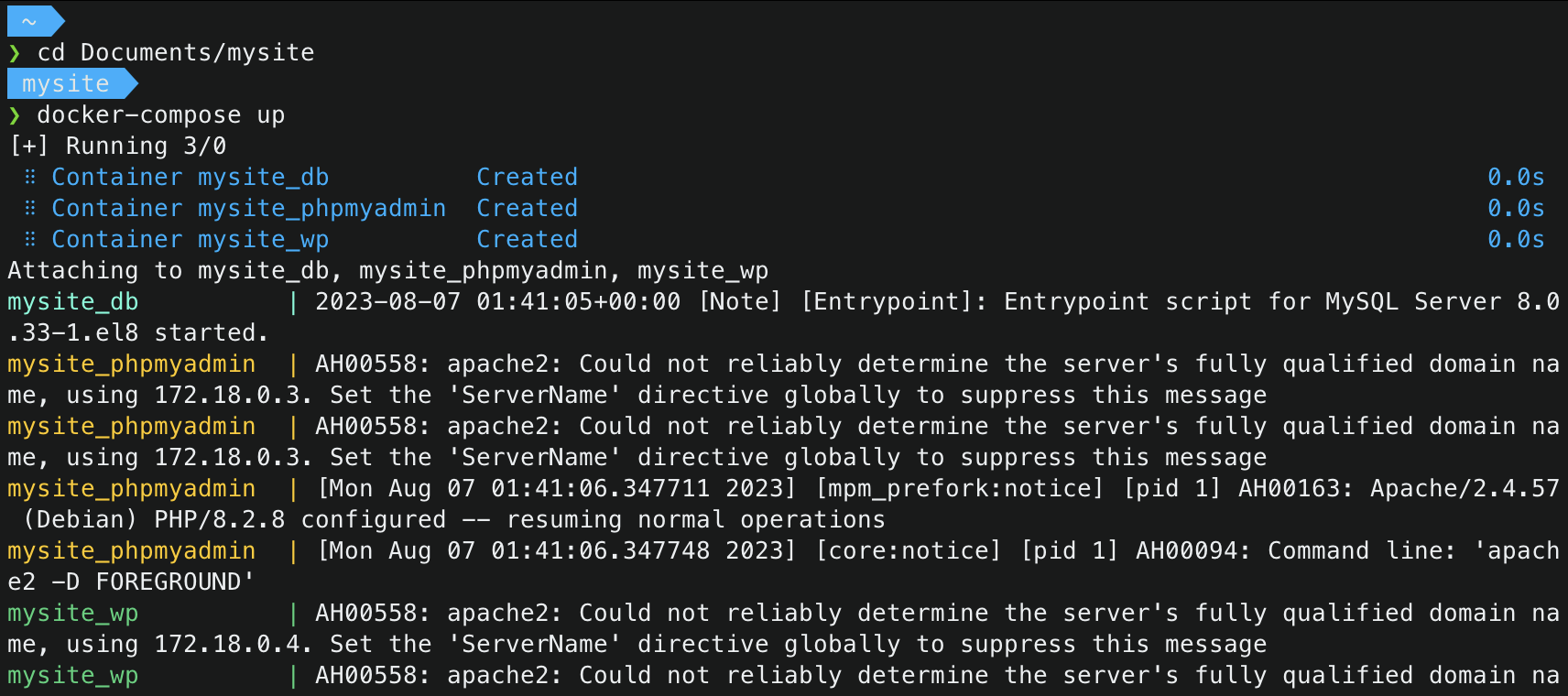
-
Verify if the new wordpress container is built successfully using your browser.
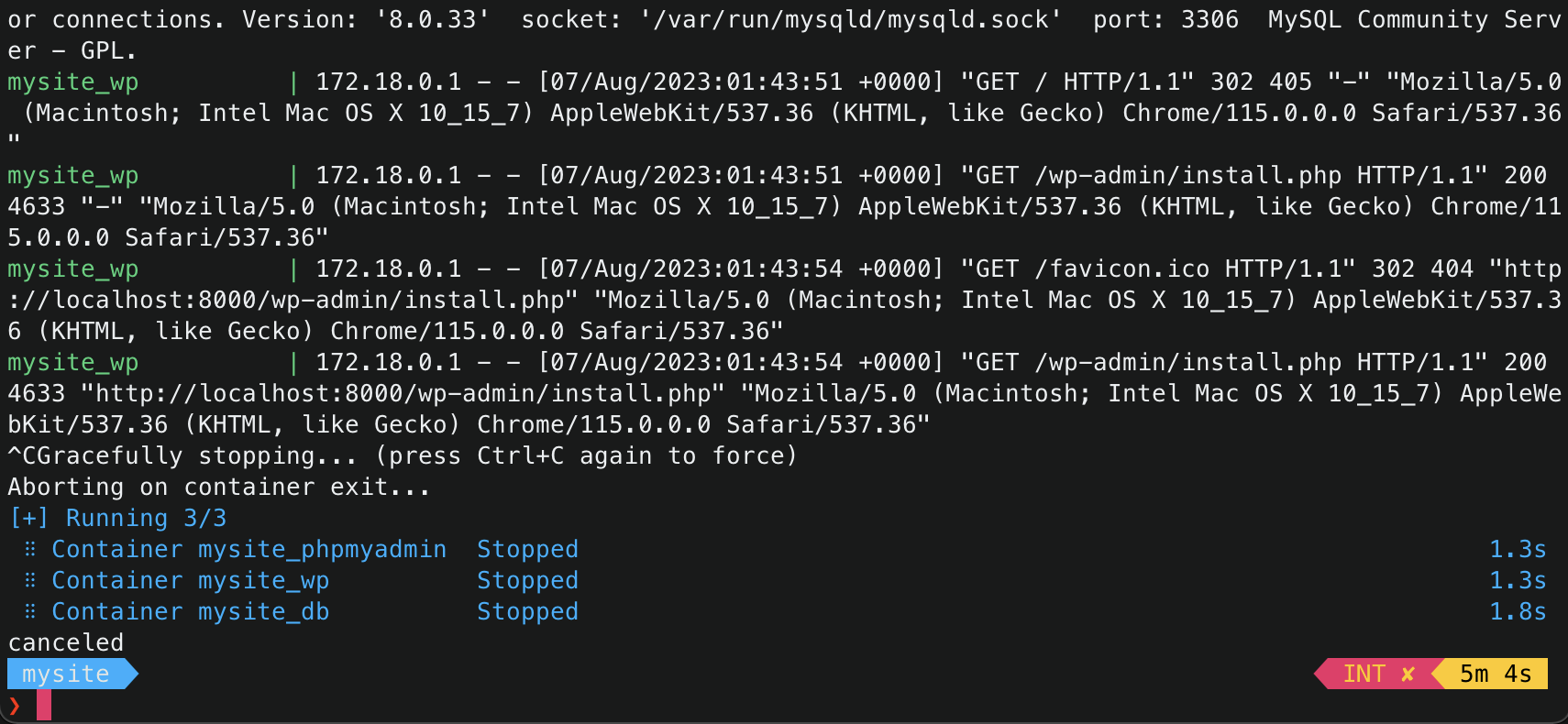
- Stop the running container
1
ctrl+c
Migrate the source code
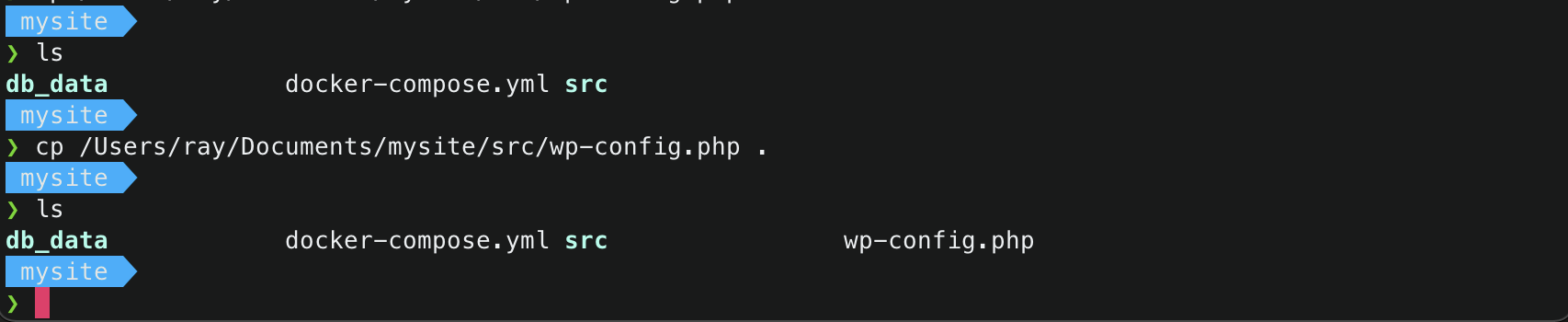
- Copy the newly built wordpress container’s
wp-config.phpfile to the root of the directory.1 2
$ cp /path/to/wp-config.php . $ ls # to verify if file has been copied
- Delete the contents of the
src/directory.1 2
$ rm -r /path/to/src/* $ ls src/ # to verify if the contents of the src/ directory has been deleted
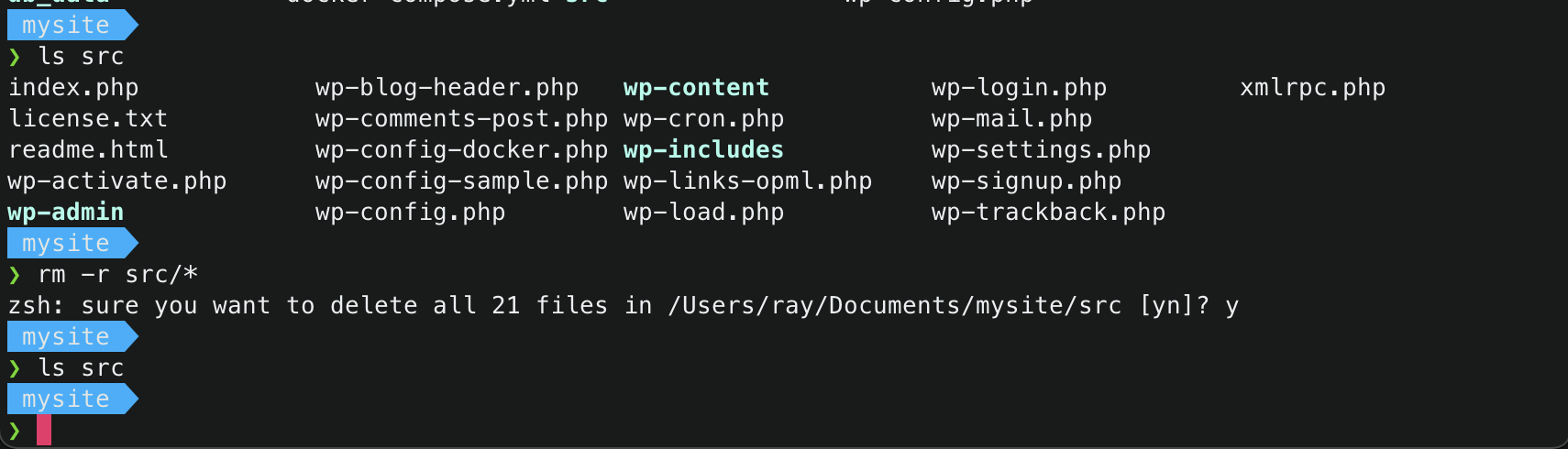
- Copy the source code of the wordpress website to migrate into the
src/directory.1 2
$ cp -r /path/to/existing/wordpress/* /path/to/new/wordpress/src/ $ ls src/ # to verify if existing wordpress source codes has been copied
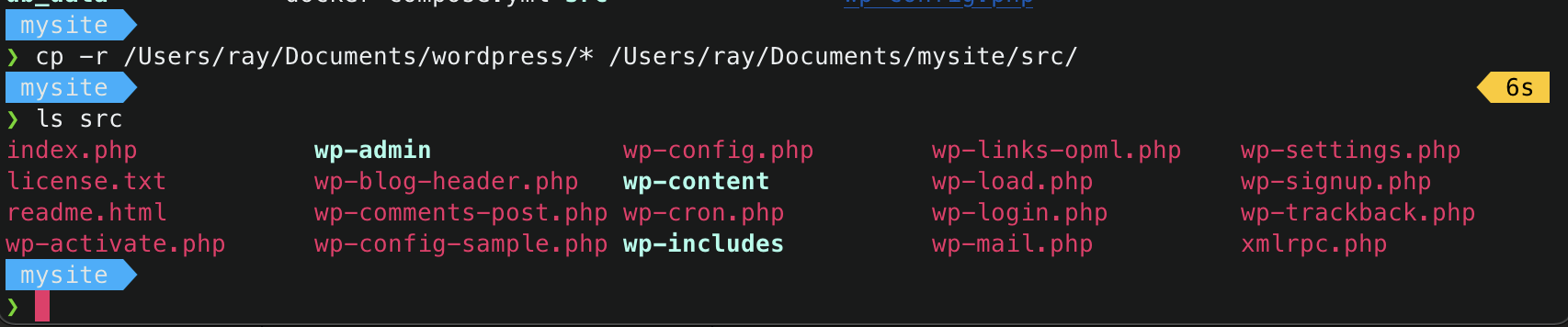
-
Copy the non-default settings of the wordpress to migrate’s
wp-config.phpfile to the rootwp-config.php(the one we copied from the original wordpress container), excluding database settings. These settings are site-specific, and is necessary to ensure your wordpress site runs perfectly. If all of the settings are default, proceed to the next step. - Replace the
src/wp-config.phpwith the./wp-config.php.1 2
$ cp -f wp-config.php src/wp-config.php $ cat src/wp-config.php # verify if files have been copied. wp-config should now have docker configuration
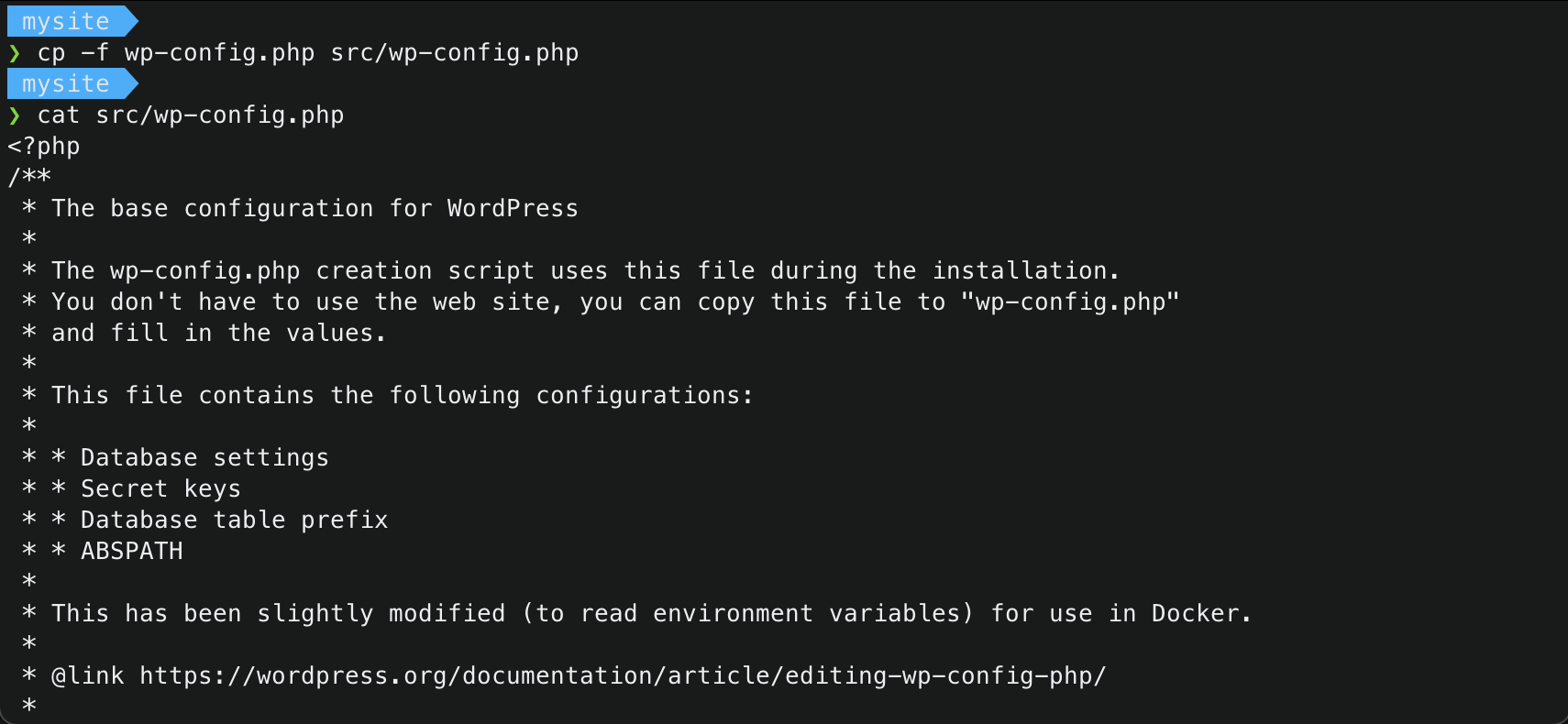
- Delete the
wp_config.phplocated in the project root, and run the docker container1 2 3
$ rm wp-config.php $ ls # to verify if wp_config.php is deleted $ docker-compose up
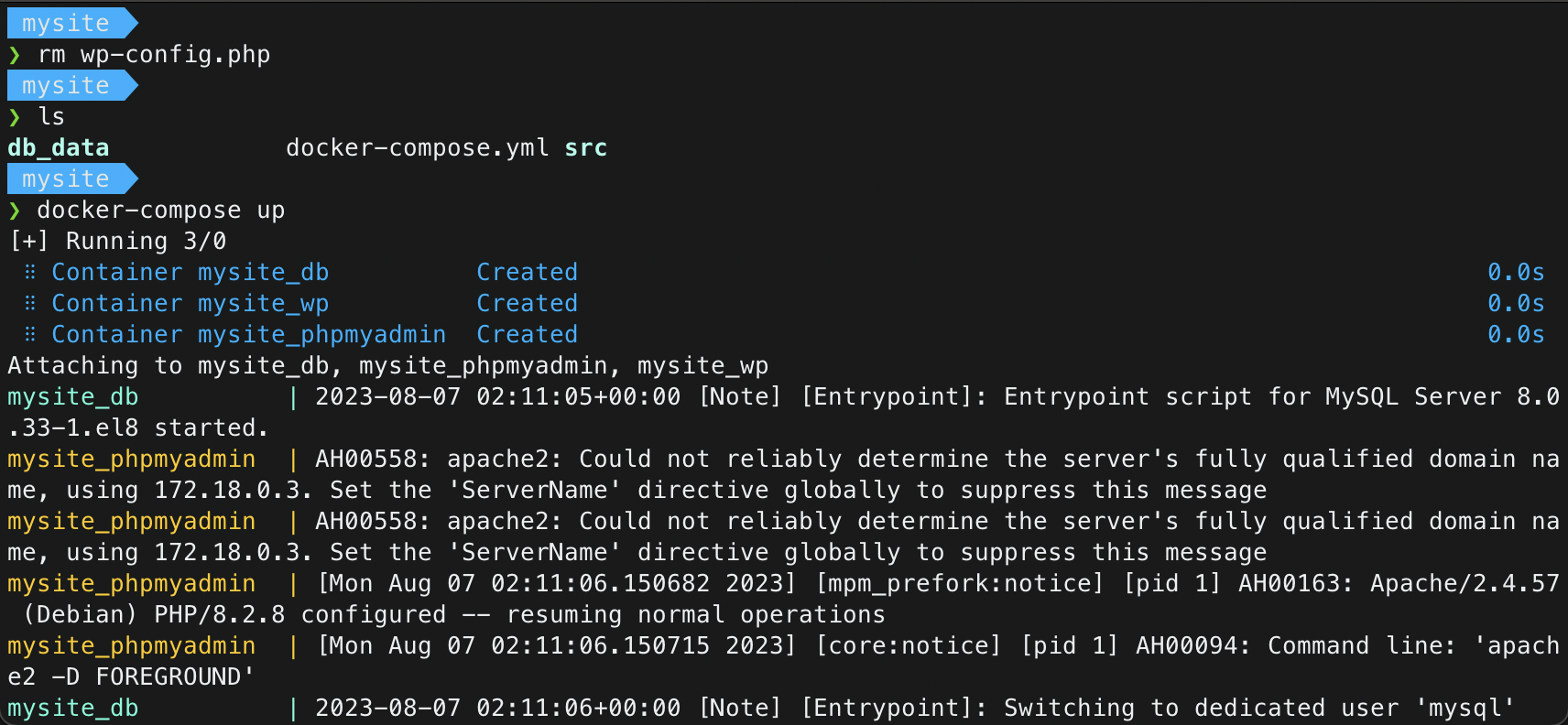
Migrate the database
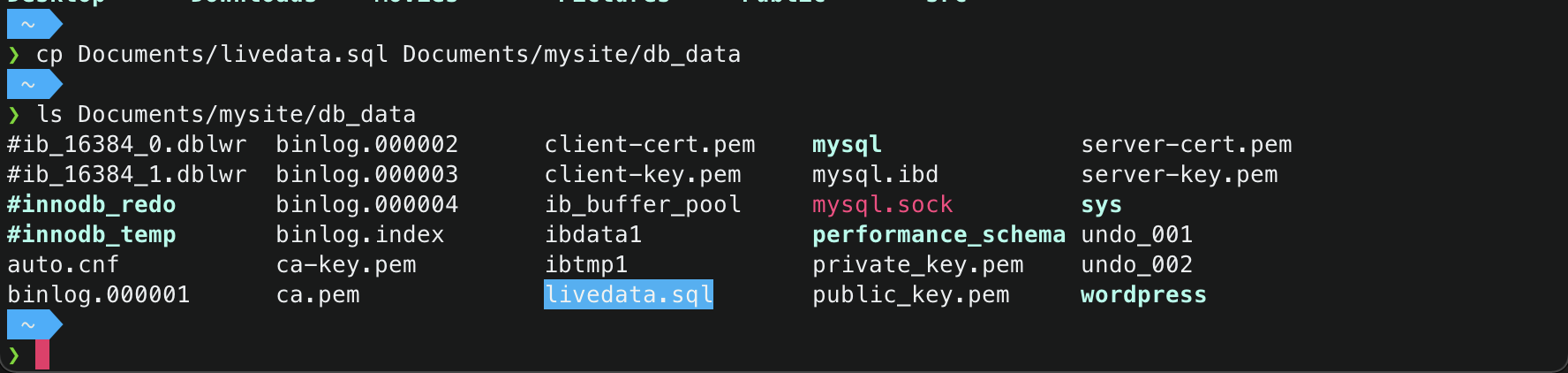
- Run a new terminal, and copy the original .sql database into the
db_data/directory of your project.1 2
$ cp /path/to/your/db.sql /path/to/your/project/db_data/ $ ls /path/to/your/project/db_data/ # to verify if the database has been copied
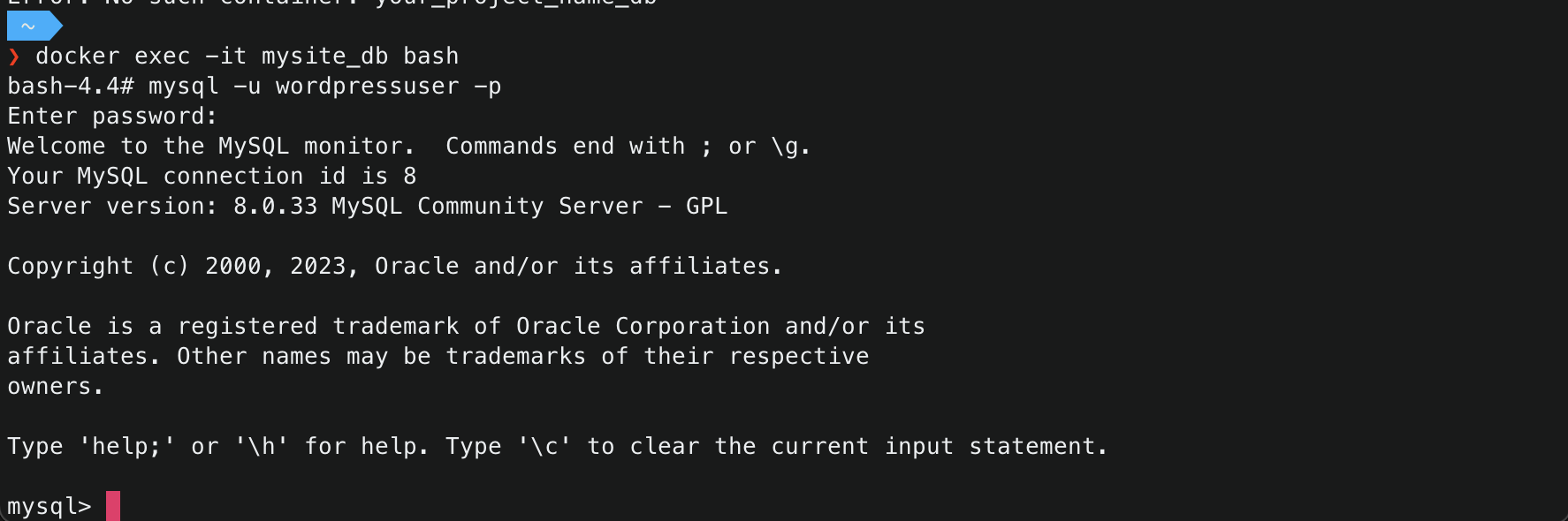
- Execute the interactive terminal of the running mysql database container, and login into mysql.
1 2 3
$ docker exec -it your_project_name_db bash bash# $ mysql -u your_MYSQL_USER -p Enter password: your_MYSQL_PASSWORD
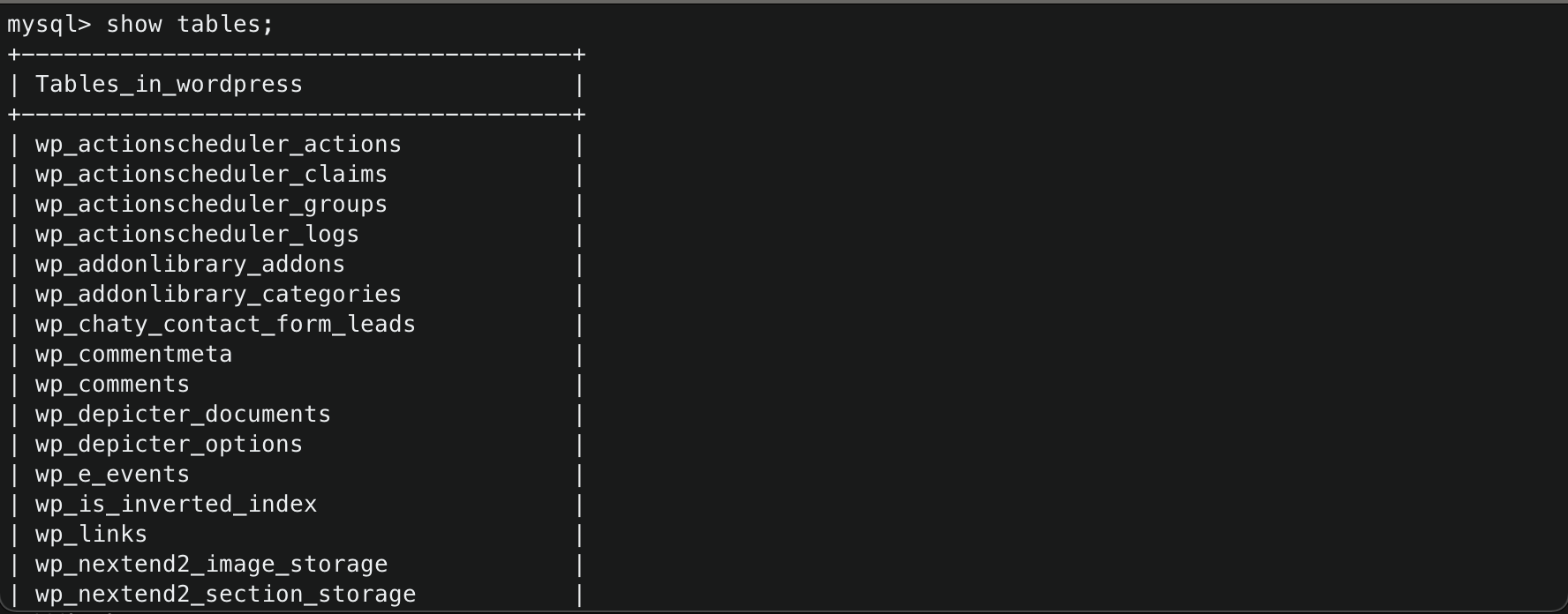
- Use
wordpressdatabase in mysql bash1 2
mysql > $ use wordpress; mysql > $ show tables; # to verify if database is empty

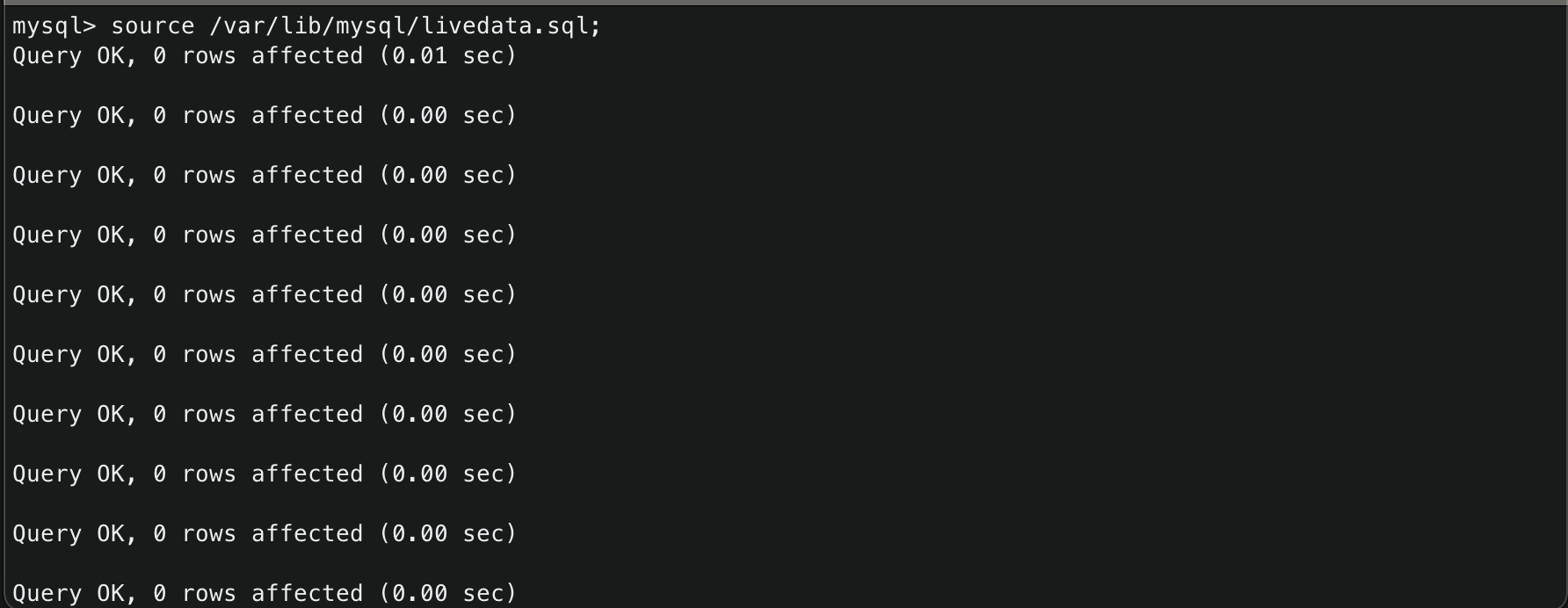
- Migrate database
1 2
mysql > $ source /var/lib/mysql/your_database_name.sql mysql > $ show tables; # check if data has been migrated
-
Open phpmyadmin in your browser
localhost:your_phpmyadmin_port, and login usingrootas username, and yourMYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDroot password. Expand thewordpressdatabase, and select thewp_optionstable.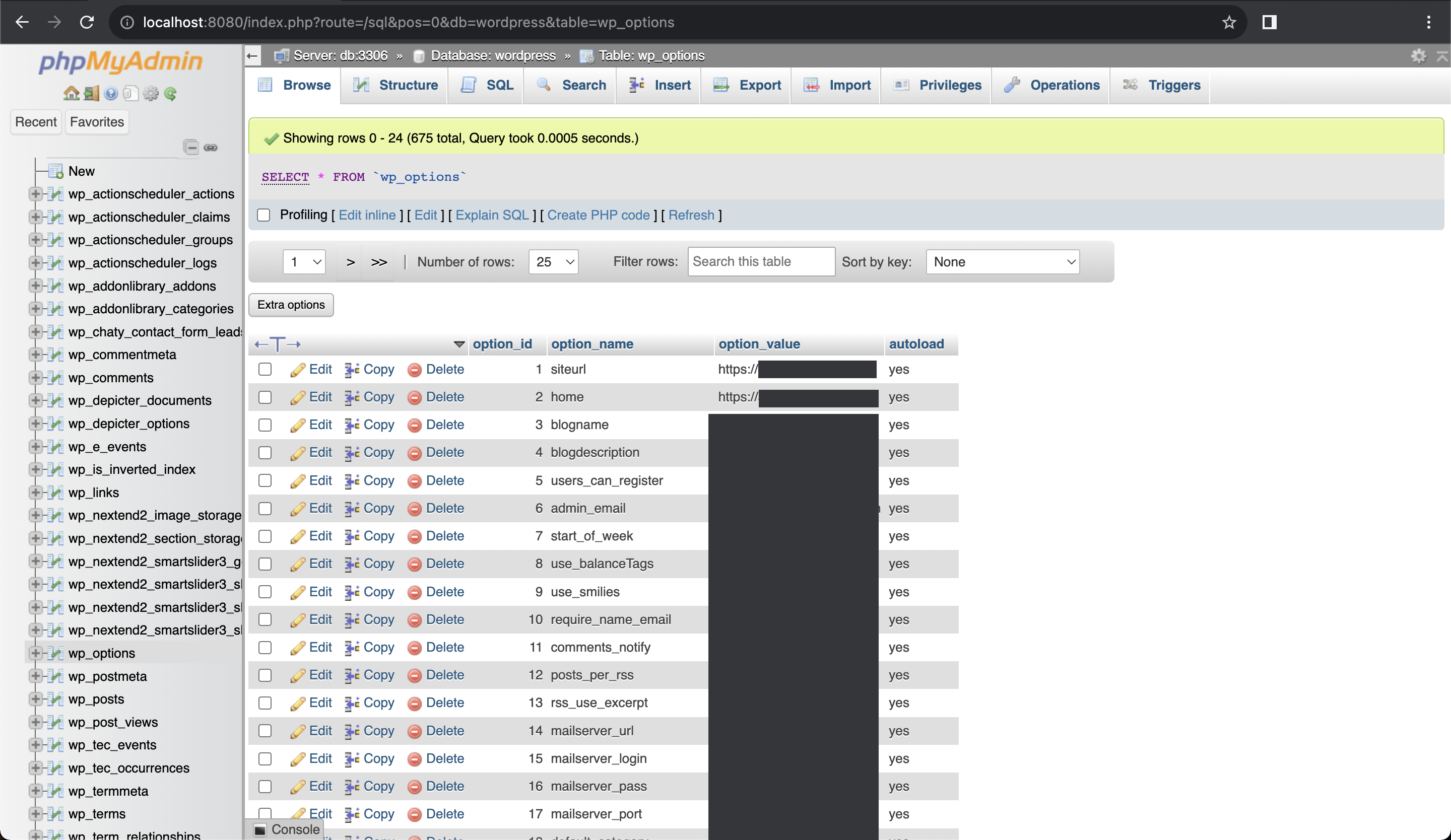
-
Click
editon the row withsiteurlandhomeoption name, and edit the value fromhttps://your_website_domainintohttp://localhost:your_wordpress_port.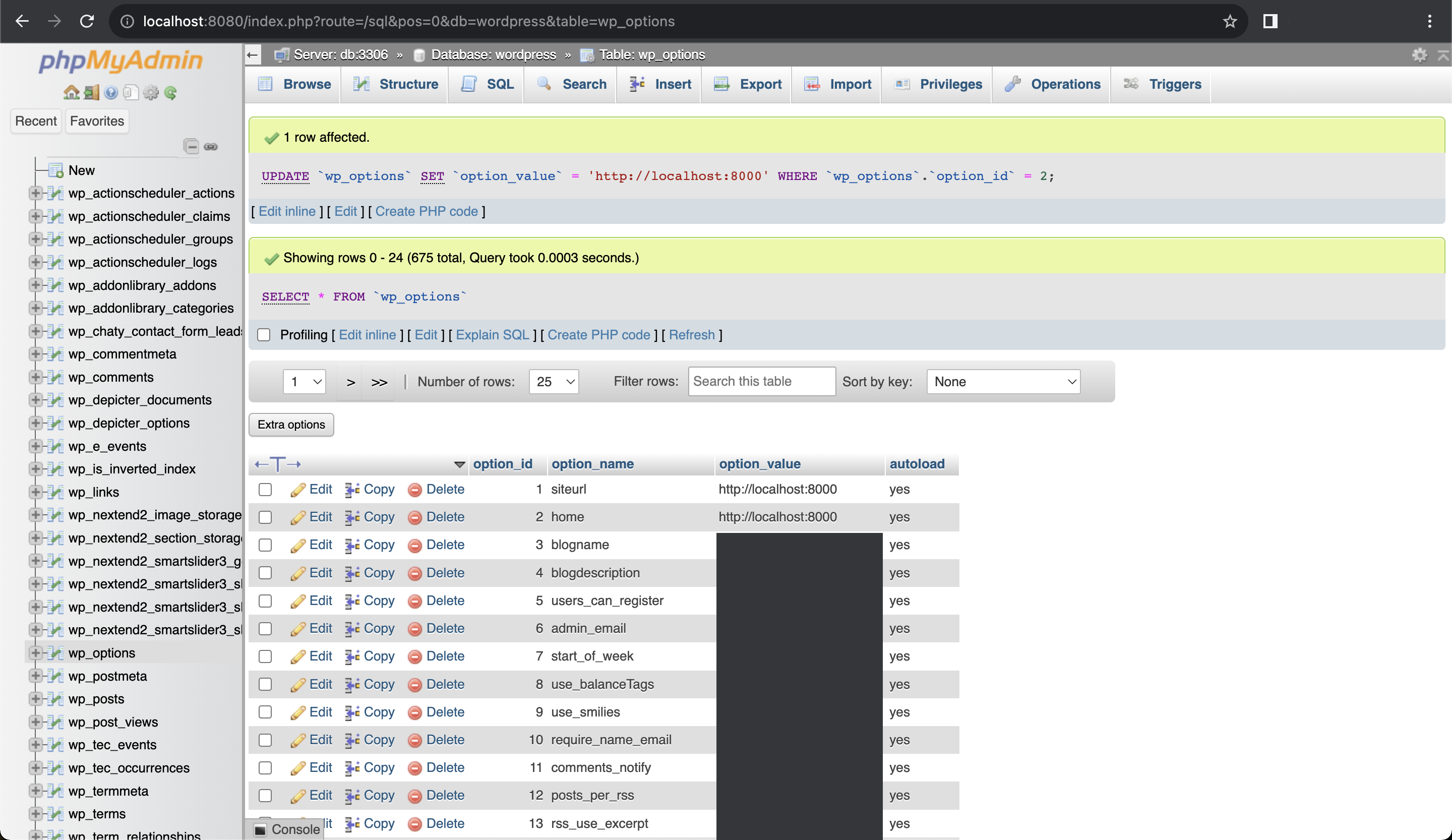
-
Refresh your browser running. You should be able to see your migrated wordpress website. You can login using your live wordpress admin credentials
-
Navigate to Setttings > Permalinks and remember the selected Permalink Structure.
- Select any permalink structure, and save. Then re-select the original permalink structure from last step and save.
Notes
*** Migrating the database steps 5 and 6 can be done through the mysql terminal directly by:
- Running the mysql container interactive terminal
$ docker exec -it your_project_name_db bash - Logging into mysql
$ mysql -u your_MYSQL_USER -p - Using the
wordpressdatabase.mysql> $ use wordpress; - Changing the value of
siteurl1
mysql> $ UPDATE `wp_options` SET `option_value` = 'http://localhost:your_wordpress_port' WHERE `wp_options`.`option_name` = 'siteurl';
- Changing the value of
home1
mysql> $ UPDATE `wp_options` SET `option_value` = 'http://localhost:your_wordpress_port' WHERE `wp_options`.`option_name` = 'home';
Done!